In biochemistry, the significant way in which metal ions are involved is in complex form. The metal ions are mostly bound to neutral macrocyclic ligands like Porphyrin ring. These macrocyclic ligands can coordinate with metal ions, without gaining or losing any charge & therefore it behaves as a neutral ligand. These ligands are often cyclic in structure and are composed of atoms, usually carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, which form the coordination site.
Within the macrocyclic ring, there are specific atoms that can act as donor atoms. These donor atoms can form coordination bonds with metal ions through their lone pairs of electrons. They have a strong affinity for coordinating with metal ions, and their binding properties can be tuned by modifying the size and nature of the macrocyclic ring and the donor atoms.
Porphyrins is one of the example of neutral macrocyclic ligand. Its chemical structure plays a crucial role in many biological and chemical processes. Porphyrins consist of four pyrrole rings linked together, forming a planar, cyclic structure. The carbon atoms within the pyrrole rings are connected by alternating single and double bonds, creating a conjugated system.
This conjugation gives porphyrin rings their distinctive color and electronic properties. There are total 11 π bonds, is highly unsaturated, highly symmetric & it follows Huckel’s Rule. Porphyrin rings are chemically active and can participate in various reactions, including oxidation-reduction reactions, coordination chemistry with metal ions, and the ability to bind to other molecules. It can also undergo Electrophilic substitution reactions.
Table of Contents
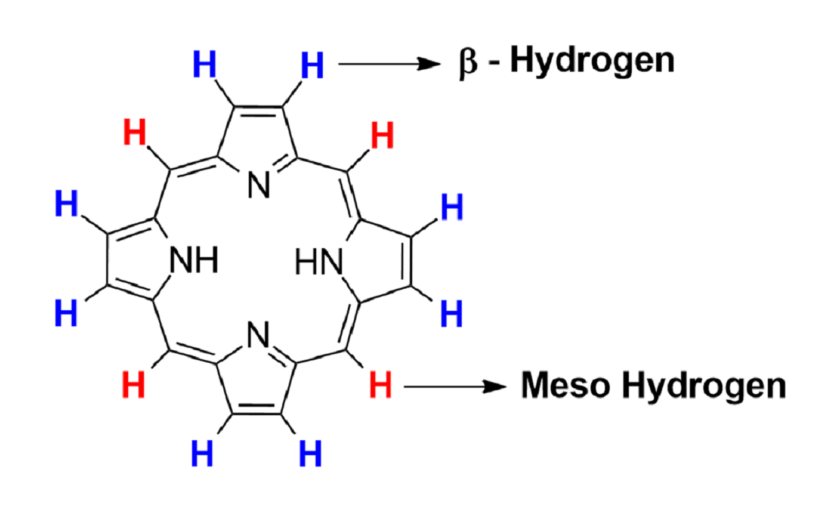
Spectral Data of Porphyrin ring
(A) 1H NMR: It shows total 3 signals; (i) Nitrogen Hydrogen signal, (ii) β – Hydrogen signal, (iii) Meso Hydrogen signal.
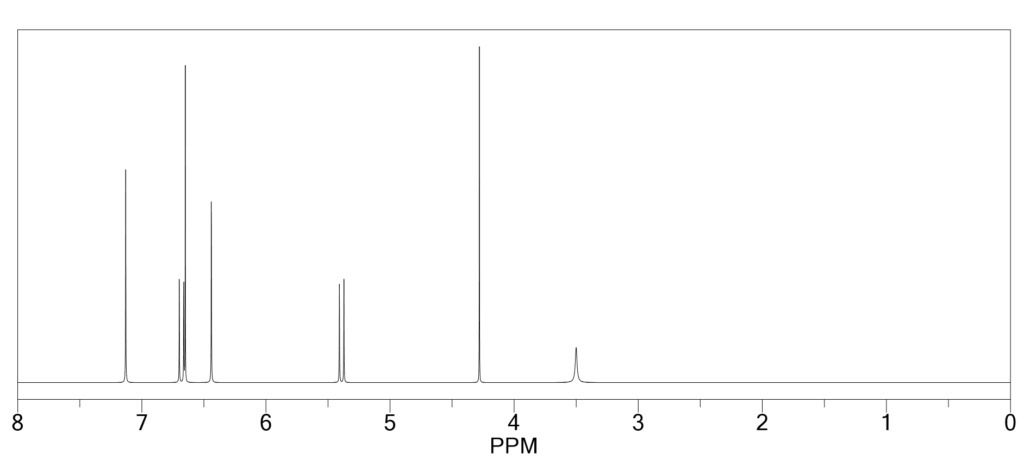
(B) IR spectroscopy: Only 1 peak is seen at 3300cm-1 that is due to stretching of N-H.
(C) UV spectroscopy: Two bands are seen Soret band which is strong & Q-band which is weak band.
Formation of Porphyrin ring
Metalloporphyrin Ring

When the metal ion is attached to the porphyrin ring, it is called as Metalloporphyrin ring. If the metal ion is iron, then it is heme unit or if magnesium then it is chlorophyll. It contains four 5-membered rings & four 6-membered rings.
Spectral Data
(A) 1H NMR: It shows only 2 signals; (i) β – Hydrogen signal (ii) Meso Hydrogen signal.
(B) IR spectroscopy: No peak of N-H stretching frequency.
(C) UV spectroscopy: Soret band becomes more broad & Q-band disappears.
Porphyrin ring in haemoglobin (Heme unit)
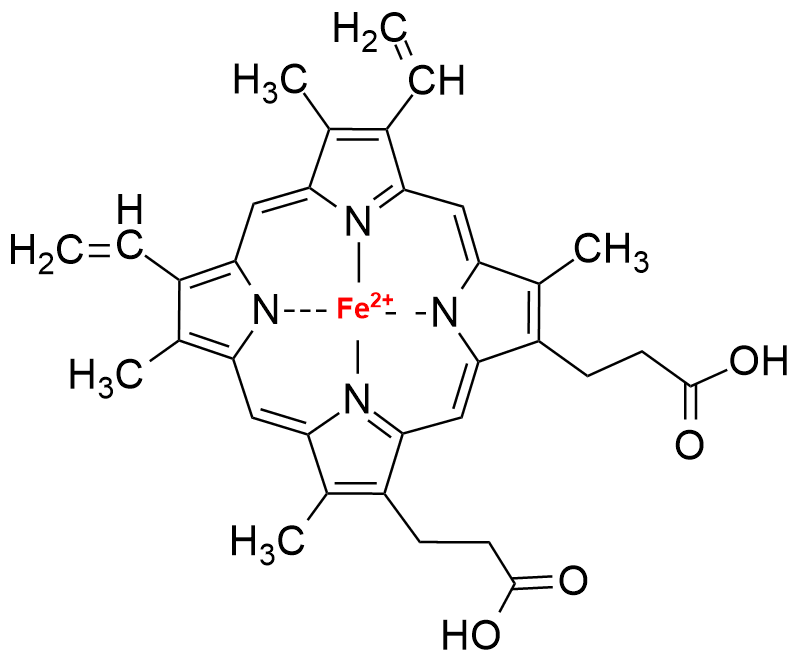
In many biological molecules, such as heme unit in haemoglobin, consists of a porphyrin ring, a planar, heterocyclic structure, with an iron (Fe) atom at its center. The iron atom can reversibly bind to oxygen (O2). This metal coordination is essential for the function of these molecules. Heme is a crucial component of haemoglobin, which transports oxygen in red blood cells. It is also found in myoglobin and various enzymes involved in oxygen binding and catalysis. Heme is responsible for the red color of blood.
Structure of chlorophyll
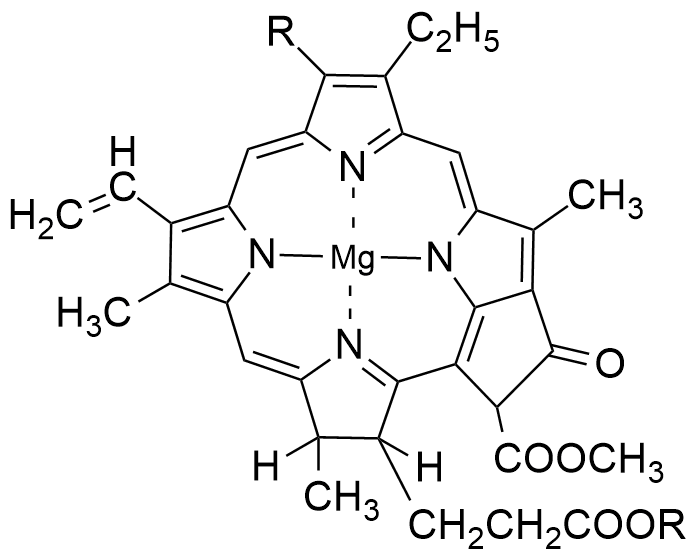
Chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants and algae. Chlorophyll molecules play a crucial role in capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Chlorophyll contains chlorin ring which has magnesium ion at its center. A chlorin ring is a chemical structure that contains four nitrogen atoms and one magnesium atom surrounded by a larger ring composed of carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and chlorine atoms & has 10 double bonds.
Chlorin is a cyclic tetrapyrrole compound and is related to other important biological molecules, such as porphyrin. The chlorin structure is characterized by its aromatic ring system, which consists of conjugated double bonds between carbon atoms. This conjugation allows chlorins to absorb light in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Vitamin B12

Vitamin B12 is a crucial water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. Vitamin B12 is a naturally occurring organometallic compound. Removal of 1 CH2 from porphyrin ring leads to Corrin ring which is a large, macrocyclic ring made up of four pyrrole-like structures. Corrin ring has 6 double bonds & is less symmetrical, less unsaturated & less conjugated. When corrin ring is joined to metal ion, it forms five 3-membered ring & three 6-membered ring. This corrin ring is the central component of the vitamin B12. Within the corrin ring, there is a cobalt ion (Co) at the center & therefore the name Cobalamin.
Vitamin B12 acts as a coenzyme, meaning it helps enzymes catalyze certain reactions in the body. The corrin ring, with its cobalt ion, is particularly important for reactions involving the conversion of methyl groups, which are crucial for processes like DNA synthesis and the metabolism of amino acids and fatty acids. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health problems like Anemia & Neurological disorders. For more Boinorganic check our category

2 comments
Comments are closed.